Infosec - CIA Triad Explained
As a part of Information Security, also referred as InfoSec, any attempt to minimize potential risks, organizations need to focus on to 3 principles: Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability. These three letters are known as CIA Triad or CIA Principles.
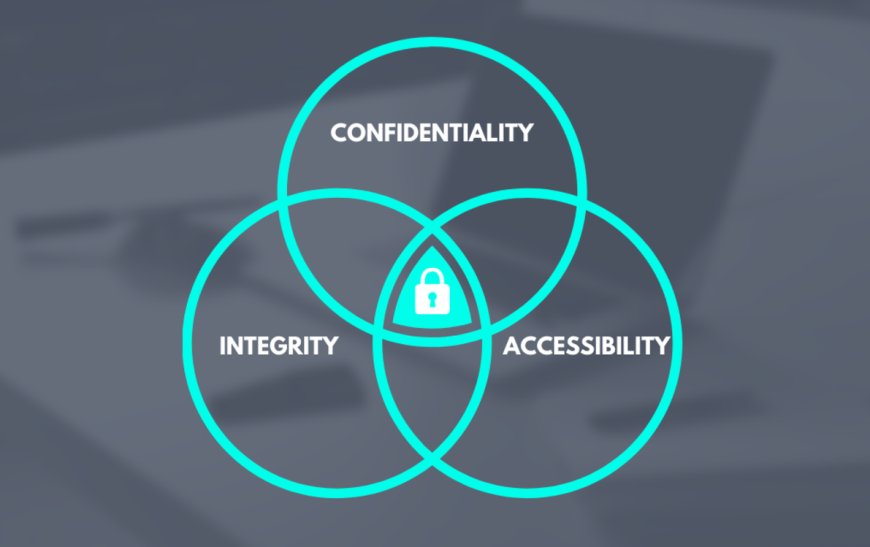
The CIA Triad is important because it represents the three core principles of information security. Maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information is essential for protecting sensitive information and ensuring the continued operation of systems and networks. These principles should function as goals and objectives for organizations' security programs.
Together, the CIA Triad helps organizations to effectively protect their sensitive information and systems from a wide range of security threats and vulnerabilities. Without implementing these three core principles, organizations can't ensure the protection of their information and systems, and can be exposed to the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and loss of service, which can have severe consequences.
CONFIDENTIALITY
Confidentiality is shortly protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure. It ensures that only authorized individuals can access and view sensitive information.
Ways to protect the confidentiality of sensitive information:
-
Access controls: Implementing strict access controls, such as user authentication and authorization, can prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive information.
-
Encryption: Encrypting sensitive information makes it unreadable to anyone without the proper decryption key. This can protect data both when it is stored and when it is transmitted over a network.
-
Data classification: Classifying data based on its sensitivity level can help determine the appropriate level of protection required. Access controls can be set in line with data classification.
-
Data Leakage Prevention (DLP) tools: DLP tools can monitor and control the movement of sensitive data within an organization, helping to prevent data breaches. But it is important to note that tools do not guarantee to prevent data breaches.
-
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS): These security measures can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information by monitoring and controlling network traffic.
-
Physical security: It includes measures such as locked cabinets, restricted access to server rooms, and other physical controls to protect sensitive information from theft or unauthorized access.
-
Employee training: Employees should be trained on how to handle sensitive information, the importance of confidentiality, and how to identify and report security incidents. Organizations should schedule training not only for incomers but also for long term members.
INTEGRITY
Integrity is preserving of the accuracy and completeness of data, and the prevention of unauthorized changes to it. It ensures that the data is not modified by unauthorized parties and that it is consistent, accurate, and reliable.
Ways to provide integrity for data:
-
Access controls: Implementing strict access controls, such as user authentication and authorization, can prevent unauthorized individuals from modifying data.
-
Hashing: Hashing is a method of creating a unique value, called a hash, for a piece of data. Any change to the original data will result in a different hash value, allowing for the detection of unauthorized changes.
-
Digital Signatures: Digital signatures provide authenticity and integrity of the data, as well as non-repudiation.
-
Backup and recovery: Regularly backing up data and having a disaster recovery plan in place can ensure that data can be restored in case of accidental or unauthorized changes. See https://kbsuperuser.com/backup-explained
-
Auditing and logging: Auditing and logging can help detect and track any changes made to data, making it easier to identify and address unauthorized changes.
-
Input validation: Ensure that data input is valid and conforms to the expected format and type.
-
Error detection and correction: Error detection and correction mechanisms can detect and correct any errors that may occur during data transmission or storage.
-
Database constraints: Database constraints, such as primary and foreign keys, can ensure that the data remains consistent and accurate.
AVAILABILITY
Availability is the ability of authorized individuals to access data and systems when they need to. It ensures that the system is up and running and that the data is accessible when required.
Ways to keep all sources available:
-
Redundancy: Implementing redundant systems, such as backup servers and power supplies, can ensure that systems remain available even if a primary component fails.
-
Load balancing: Load balancing distributes the workload across multiple servers, reducing the risk of any single server becoming a bottleneck and causing the system to become unavailable.
-
Disaster recovery: Having a disaster recovery plan in place can ensure that systems and data can be quickly restored in case of a disaster or outage. See https://kbsuperuser.com/disaster-recovery-planning-explained
-
Monitoring and maintenance: Regularly monitoring systems and performing preventative maintenance can help detect and resolve issues before they cause an outage.
-
Backup power: Having backup power sources, such as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and generators, can ensure that systems remain available during power outages.
-
Network security: Network security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs), can help prevent unauthorized access to systems and data.
-
Cloud-based services: Cloud-based services can provide additional scalability, disaster recovery, and security features to ensure the availability of the systems and data.
-
Business continuity planning: Business continuity planning helps organizations to identify and mitigate the risks that could disrupt the availability of their systems and data, and also have a plan in place to quickly restore them.
APPLYING CIA TRIAD to ORGANIZATION
-
Conduct a risk assessment: Identify what information and systems are critical to the organization and assess the risks to their confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
-
Develop a security plan: Use the information from the risk assessment to develop a security plan that addresses the identified risks and includes specific controls for maintaining confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
-
Implement security controls: Implement the controls identified in the security plan, such as access controls, encryption, data classification, and network security.
-
Continuously monitor and update: Continuously monitor the systems and data to ensure that the security controls are functioning as intended and update them as needed to address new or emerging threats.
-
Training and awareness: Train employees on security best practices and the importance of maintaining confidentiality, integrity, and availability, and make them aware of their role in protecting the organization's information assets.
-
Compliance: Ensure that the organization is following relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards related to information security.
-
Testing: Regularly testing security controls and incident response plans can help organizations identify and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
-
Incident response: Having an incident response plan in place and regularly testing it can help organizations quickly respond to and recover from security incidents.
What's Your Reaction?